Extension > Garden > Diagnose a problem > What's wrong with my plant? > Vegetable > Potato > Flecks, spots, streaks, or blotches on stem
Potato > Stem > Flecks, spots, streaks, or blotches on stem
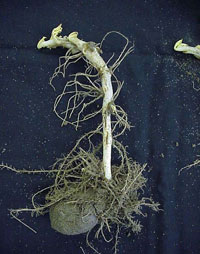
1 of 7
Early Blight
Alternaria solani
- Stem lesions are dark, slightly sunken areas
- Leaf spots are round, brown with target like rings inside
- When severe many leaf spots grow together resulting in large brown patches and leaves turn yellow
- Potato tubers develop dark, sunken spots surrounded by a purplish brown raised border
- Rough, corky dry tissue can be seen below tuber spots when cut open
- More prevalent in warm and humid weather
- More information on managing plant diseases in the home garden
2 of 7
Late Blight
Phytophthora infestans
- In wet weather, leaves, stems and petioles rapidly turn brown and shrivel
- Large irregular olive to brown leaf spots that are not restricted by leaf veins
- Powdery white fungal growth can be seen on infected tissue in wet weather
- Irregular sunken, dull brown to purple lesions around the eyes on potato tubers
- Inside of potato tuber has a reddish-brown dry rot
- More prevalent in years of cool and wet weather
- More information on managing plant diseases in the home garden
3 of 7
White Mold
Sclerotinia sclerotiorum
- Elongated tan dry lesions form on stems
- Leaves wilt but remain green
- Fluffy white fungal growth and small hard black fungal sclerotia can be found on or in infected stems
- More information on managing plant diseases in the home garden
4 of 7
Black Dot
Colletotrichum coccodes
- Sunken dark brown to black lesion on stem that turns white in the center with age
- Irregular patches of gray discoloration on surface of the potato tuber
- Many pinprick sized black dots can be seen on infected stems and tubers (handlens is helpful)
- Leaves may have random brown spots, or may yellow and wilt due to infection of stem and roots
- More information on Black Dot
5 of 7
Blackleg and Soft Rot
Pectobacterium carotovora
- Brown to black slimy sunken lesions on stems, most common starting at the soil line
- Seed potato may rot in the soil, plants do not emerge
- In severe cases, plant is stunted, with yellow and wilted leaves
- Tuber flesh is white, soft and rotted. In severe cases the entire tuber rots away, leaving on the skin
- Favored by cool wet weather
- More information on Blackleg and Soft Rot
6 of 7
Black Scurf/Rhizoctonia Canker
Rhizoctonia solani
- Stem has a white to gray flaky growth just above the soil line.
- Underground stems and roots have brown, sunken dry spots
- Late or no emergence, have few stems, and poor growth
- Small hard black spots stick to the skin of the tuber like dirt that won't wash off
- Tuber production is low, tubers may be small and deformed
- In severe cases, small green tubers form on the stem above ground
- Most problematic in cool wet soils
- More information on Black Scurf/Rhizoctonia Canker
7 of 7
Corky Ring Spot
Tobacco Rattle Virus
- Stems may be mottled green and yellow
- Leaves may have no symptoms or have yellow rings, spots and arcs
- Brown rings and arcs form on the skin and in the flesh of tubers
- Potato tubers can be cracked and malformed if infections comes in early
- More information on Corky Ring Spot