Extension > Garden > Diagnose a problem > What's wrong with my plant? > Evergreen Trees and Shrubs > Pine > Needles half green, half brown
Pine > Needles > Needles half green, half brown
1 of 5
De-icing salt
- Needles brown from the tips down
- Affected needles more common on side of tree facing the source of salt
- Premature needle drop
- Buds or candles may be killed
- Reduced growth with prolonged contact
- More information on De-icing salt injury
2 of 5
Dothistroma needle blight
Mycosphaerella pini
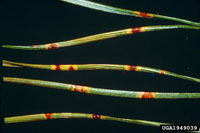
- Tan to brown spots on 1 yr. or older needles turn red in the sun
- Needle tips are tan, bases remain green, scattered with brown or red spots
- Tiny, raised, black pimple-like fungal spore producing structures form on dead needle tissue
- Diseased needles turn completely brown and eventually drop
- Lower portions of tree are most severely affected
- Most common on Austrian and ponderosa pine; Scots pine has some resistance
- Lab analysis is often necessary to distinguish Dothistroma needle blight from Brown spot
- More information on Dothistroma needle blight
3 of 5
Brown spot needle blight
Mycosphaerella dearnessii
- Small yellow to brown, resin-soaked spots form on 1 yr old needles in June-Aug
- Often needle tip is killed and turns tan, base of needle remains green with random yellow to brown spots
- Tiny, raised, black pimple-like fungal spore producing structures form on dead needle tissue
- Diseased needles fall off in autumn
- Infections are most common on lower branches
- Outbreaks favored by prolonged wet weather in June and July
- Scots pine most commonly infected; many Minnesota pines are susceptible
- Lab analysis is often necessary to distinguish Brown spot from Dothistroma needle blight
- More information on brown spot needle blight
4 of 5
Winter injury
- Needles turn brown in late winter-early spring
- Needles turn brown from the tip down, needle base often remains green
- Needles at the tip of the branch are more severely discolored than those close to the trunk
- Damage often only on one side of the tree
- Common on trees exposed to wind and sun or light reflecting off buildings
- Damage most severe at the top of the tree, branches covered by snow are unaffected
- More information on Winter injury
5 of 5
Scleroderris canker
Gremmeniella abietina
- Needle clusters turn brown from the base up and are easily pulled off the branch
- Infected needles fall off in summer
- Buds on infected twigs fail to open
- Cutting into branch below discolored needles reveals yellow-green discoloration
- Cankers can kill branches or move into main stem and become perennial
- Damage is greatest to small
- Jack and red pine most commonly affected
- More information on Scleroderris canker