Extension > Garden > Diagnose a problem > What's wrong with my plant? > Evergreen Trees and Shrubs > Pine > Yellow to reddish brown needles
Pine > Needles > Yellow to reddish brown needles on part to most of the tree
1 of 7
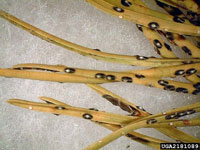
Glyphosate herbicide damage
(e.g. Roundup)
- Needles retain shape but turn pale yellow to reddish-brown
- If damage is severe, needles drop and branches may die
- Symptoms occur a few days to several weeks after herbicide application
- Dead or dying weeds expressing similar symptoms may be present nearby
- More information on Glyphosate herbicide damage
2 of 7
Air pollution
- Yellow, brown or dead needles
- May effect entire needle or cause spots or areas of discoloration
- May effect entire tree or be noticeably confined to one or more areas
3 of 7
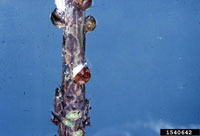
Pine needle scale
Chionaspis pinifoliae
- Adults are small white, 1/8 inch long flecks on needles; visible all year
- Immature crawlers are active in May; are reddish-brown and the size of pinhead
- Light infestations generally don't show symptoms
- Moderate to heavy infestations can cause needles to discolor and even branches to die
- Attacks all pine as well as other evergreens
- More information on Pine needle scale
4 of 7
Pine tortoise scale
Toumeyella parvicornis
- Moderate feeding can cause needles to yellow and become shortened
- Heavy infestations can cause shoots and branches to die back
- Feeding produces honeydew which can cause sooty mold
- Individual scales are reddish-brown, helmet-shaped and up to ¼ inch long when mature
- More information on scale insects
5 of 7
Pine spittlebugs
Aphrophora parallela
- White foamy mass on twigs and needles
- Small (up to ¼ inch), black and pale yellow nymphs on underside of needles
- Light infestations generally do not cause noticeable symptom
- Moderate to severe feeding can cause needle yellowing, shoot flagging and twig dieback
- Prefers Scots, Austrian and eastern white pine
- More information on Pine spittlebugs
6 of 7
Saratoga spittlebugs
Aphrophora saratogensis
- Yellowing needles eventually turn reddish-brown and die
- Flagging shoots/branches (occasionally)
- Favors plantations of young red, jack and Scots pine, occasionally white pine and balsam fir in; older trees less susceptible to attack
- Generally only a problem in the northern 1/3 of Minnesota
- Adults are tannish, wedge-shaped, from ¼ -3/8 inch long
- More information on Saratoga spittlebugs
7 of 7
Black pineleaf scale
Nuculaspis californica
- Individual needles discolored red or yellow
- Severe infestations can kill branches or even entire trees
- Stressed pines of all species are particularly susceptible
- Insects are tiny (a little more than 1/16 of an inch long) gray to black, oval shells
- Often found with pine needle scale
- More information on Black pineleaf scale