Extension > Garden > Diagnose a problem > What's wrong with my plant? > Evergreen Trees and Shrubs > Pine > Spots or bands on needles
Pine > Needles > Spots or bands on needles
1 of 5
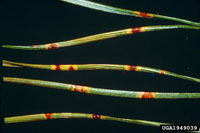
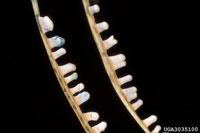
Pine needle scale
Chionaspis pinifoliae
- Adults are small white, 1/8 inch long flecks on needles; visible all year
- Immature crawlers are active in May; are reddish-brown and the size of pinhead
- Light infestations generally don't show symptoms
- Moderate to heavy infestations can cause needles to discolor and even branches to die
- Attacks all pine as well as other evergreens
- More information on Pine needle scale
2 of 5
Dothistroma needle blight
Mycosphaerella pini
- Tan to brown spots on 1 yr. or older needles turn red in the sun
- Needle tips are tan, bases remain green, scattered with brown or red spots
- Tiny, raised, black pimple-like fungal spore producing structures form on dead needle tissue
- Diseased needles turn completely brown and eventually drop
- Lower portions of tree are most severely affected
- Most common on Austrian and ponderosa pine; Scots pine has some resistance
- Lab analysis is often necessary to distinguish Dothistroma needle blight from Brown spot
- More information on Dothistroma needle blight
3 of 5
Brown spot needle blight
Mycosphaerella dearnessii
- Small yellow to brown, resin-soaked spots form on 1 yr old needles in June-Aug
- Often needle tip is killed and turns tan, base of needle remains green with random yellow to brown spots
- Tiny, raised, black pimple-like fungal spore producing structures form on dead needle tissue
- Diseased needles fall off in autumn
- Infections are most common on lower branches
- Outbreaks favored by prolonged wet weather in June and July
- Scots pine most commonly infected; many Minnesota pines are susceptible
- Lab analysis is often necessary to distinguish Brown spot from Dothistroma needle blight
- More information on brown spot needle blight
4 of 5
Pine needle rust
Coleosporium asterum
- Yellow to orange spots or bands on needles
- Late spring to early summer, raised white tubes form on needle spots, these break open and release orange spores
- Lower branches most severely effected with browning and needle loss
- Many two and three needle pines are susceptible
- Also infects nearby members of the aster family
- Pine needle rust is a minor stress on the tree and no management is required
- More information on pine needle rust
5 of 5
Lophodermium needle cast
Lophodermium seditiosum
- Yellow to brown spots appear in late summer or early fall
- 1 yr old needles turn brown in spring
- Gray to black ovals with a slit down the center (fungal spore producing structures) can be seen on dead needles
- Infected needles drop prematurely during the summer
- Lower branches and small trees most severely effected
- Common on red, Austrian and Scots pine
- More information on Lophodermium needle cast