Extension > Garden > Diagnose a problem > What's wrong with my plant? > Evergreen Trees and Shrubs > Pine > Dead or dying seedlings
Pine > Seedlings > Dead or dying seedlings
1 of 5
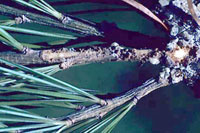
Diplodia shoot blight
Diplodia pinea
- New needles are brown, short and often glued together with resin
- Cankers are resin coated flattened areas on branches
- Needles and branch beyond canker turn brown and dies
- Tiny, black, pimple-like fungal structures on dead needles and pine cones
- Infected shoots and dead branches occur throughout the tree but most commonly in lower canopy
- Cankers and dead needles can appear rapidly after wounding from hail, drought or other stress
- Olive to dark brown streaking in sapwood below cankers
- Common on Austrian, red and Scots pine
- More information on Diplodia shoot blight
2 of 5
White grubs
Phyllophaga spp.
- Wilted, dying or dead seedlings
- Fibrous roots missing from affected seedlings
- Common in grassy areas; all conifers affected
- C-shaped white larva with brown head; conspicuous legs; grow to 1 inch long
- More information on White grubs
3 of 5
Northern pine weevil
Pissodes approximatus
- Dead 2 – 4 year old seedlings
- Attacks all pines, particularly seedlings with heavy grass competition
- Larvae about 1/3 inch long, white and feed under bark
- Cocoons made of wood chips (chip cocoons) found under bark
- Adult weevils about 1/3 inch long, brown with small white spots and typical weevil "snout"
- More information on Northern pine weevil
4 of 5
Sirococcus shoot blight
Sirococcus conigenus
- Needles turn brown, wilt and droop
- Young shoots wilt and curl into a shepherd's crook
- Brown to black raised bumps can be seen on wilted needles and on shoots at the base of the needle in the fall or spring following the appearance of symptoms
- Older needles remain unaffected
- Common in cool, wet summers
- Infection often starts in the lower branches and moves up
- Common on red, jack and Scots pine; Austrian and eastern white pine are resistant
- Also infects spruce, fir and larch
- More information on Sirococcus shoot blight
5 of 5
Armillaria root rot
Armillaria spp.
- Infected trees have reduced growth, discolored needles, thin canopies; produce large amount of cones and eventually die
- Flat white sheets of fungal growth (mycelial fans) between the bark and sapwood at the base of infected trees
- Thick, black shoestring-like fungus can sometimes be seen under the bark at the root collar and in the soil near the base of the tree
- Base of the tree may be encrusted in resin
- Wood is decayed, white, soft and spongy, beginning with the roots and may extend from the base of the tree well up into the trunk
- Trees frequently break or fall over in storms
- Clusters of honey-colored mushrooms may grow at the base of the tree in fall
- More information on Armillaria root rot