Extension > Garden > Diagnose a problem > What's wrong with my plant? > Fruit > Raspberry > Wilted tips/loss of leaves
Raspberry > Canes > Wilted tips/loss of leaves
1 of 7
Raspberry Cane Borer
Oberea bimaculata
- Wilting may be evident at the tips of new shoots
- Two rings of punctures about ½ inch apart, and located 4-6 inches below the growing tip, are apparent where the beetle has laid eggs
- Adult is slender, ½ inch long, black, with yellow stripes and a yellow head with two black spots
- Full grown larvae are ¾ inch long, cream colored, and legless
- Adults are active in June
- Larvae can be found inside canes from mid summer through fall
- More on raspberry cane borer
2 of 7
Raspberry Cane Maggot
Pegomya rubivora
- Feeding by maggots inside cane causes the young shoots to wilt
- Damage occurs in early spring
- Adult is a small, gray fly about two-thirds
- More on raspberry cane maggot
3 of 7
Winter Injury
- Leaves of mature canes wilt and die at the top of the cane only
- Flowering is sparse; flowers and fruit may form and fail to develop
- New canes will be healthy
- More information on Winter Injury
4 of 7
Verticillium Wilt
Verticillium albo-atrum
- Leaves turn yellow and fall off from the bottom of the plant up
- Canes turn blue or have blue streaks
- Reddish brown streaks may be seen in the center of infected canes if bark is peeled away
- Black raspberries die in 1-3 years
- Red raspberries may survive many years but with reduced vigor
- More information on Verticillium Wilt
5 of 7
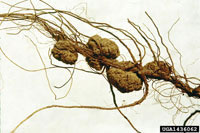
Crown Gall and Cane Gall
Agrobacterium tumefaciens, Agrobacterium rubi
- Wilting may be evident
- Spongy white tumor-like galls on the cane, roots, and crown
- Older galls are brown to black and hard
- Poor growth and fruit production may be seen on severely infected canes
- More information on crown gall
6 of 7
Cane Blight
Leptospaeria coniothyrium
- Shoots wilt and die as fruit develops
- Dark streaks on cane, always around a wound
- More information on Cane Blight
7 of 7
Fire Blight
Erwinia amylovora
- Tips of young canes wilt, become blackened, and curl over into a “shepherd’s crook”
- Developing berries become hard and dry
- Leaf veins and petioles turn black, and canes die from top down
- More information on caring for raspberries