Extension > Garden > Diagnose a problem > What's wrong with my plant? > Fruit > Strawberry > Stunted plant
Strawberries >Whole Plant > Stunted plant
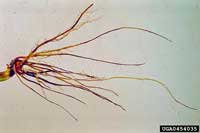
1 of 6
Black Root Rot
Rhizoctonia sp. Pythium sp. and Fusarium sp.
- After first year, plants in a field showing reduced vigor, often in low or wet spots or in areas where the soil is compacted
- Roots appear ‘rat tailed’ and do not have fine fibrous root hairs
- Irregular black patches occur along the length of the fleshy white roots
- Interior of infected older woody roots turns black
- Common in areas where strawberries have been grown for many years
- More information on Black Root Rot
2 of 4
Red Stele
Phytophthora fragariae
- Plants start wilting and dying in the lower portions of the strawberry planting
- Roots appear ‘rat tailed’ and do not have fine fibrous root hairs
- Root tips are soft, discolored and rotten
- If the white root above the rotten tip is cut lengthwise, the root core (or stele) will appear to be dark red
- Common and most destructive in heavy clay soils or low wet areas
- Favored by cool, wet spring weather
- More information on Red Stele
3 of 6
Nitrogen Deficiency
- Leaves turn yellow, most obvious on older, lower leaves
- Plants grow slowly, produce few leaves and daughter plants
- Plant produce few and small berries
- Common in sandy soils
- More information on Nitrogen Deficiency
4 of 6
Cold Damage
- Plants exhibit poor growth in early spring
- Flowering is sparse
- When cut in half, the interior of the main stem (crown) is brown
5 of 6
Glyphosate Herbicide Injury
- Yellowing appears suddenly, and is restricted to the veins
- Plant appears stunted because of small leaves crowded close together
6 of 6
White Grubs
Phyllophaga spp.
- Plant is stunted, will wilt, and eventually dies
- Grubs feed on roots throughout the summer months
- Grubs have a white body color, brown head capsule, and c-shaped body
- Occurs in plantings that were previously grassy
- Adults do not feed on strawberries
- More information on White Grubs