Extension > Garden > Diagnose a problem > What's wrong with my plant? > Vegetable > Broccoli > Yellowing leaves
Broccoli > Leaves > Yellowing leaves
1 of 7
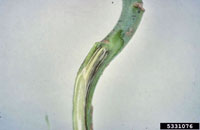
Black Rot
Xanthomonas campestris
- Yellow V-shaped lesions develop on margin of leaves, the point of the v follows a vein towards the base of the leaf
- As infection continues, leaves wilt, turn yellow and eventually turn brown and die
- Black veins can be seen in infected leaves, petioles and stems
- Sticky yellowish liquid bacterial ooze may be seen if infected veins are cut
- Disease favored by hot, humid conditions
- More information on Black rot
2 of 7
Fusarium Wilt (Yellows)
Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. conglutinans
- Plant has a yellowish-green overall color that often occurs only on one side of the plant
- Lower leaves yellow first, yellowing progresses up the plant
- Affected leaves wilt, eventually turn brown, become dry and brittle, and may fall off
- Stem and midrib of the leaf curve to one side
- Veins in affected leaves are yellowish brown
3 of 7
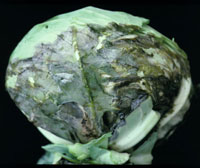
Bottom Rot/Head Rot
Rhizoctonia solani
- Leaves turn yellow/brown and wilt
- Bottom of lower leaf develops sunken, black, and elliptical lesions parallel to the midrib of the leaf
- Dark cobweb-like or cotton-like fungal growth develops between diseased leaves
- Disease may be limited to the lowest leaves or may start at the bottom of the plant and move up through wrapper leaves into the cabbage head
4 of 7
Club Root
Plasmodiophora brassicae
- Leaves turn pale yellow, wilt during hot, sunny days, and recover at night
- Young plants may die
- Older plants fail to develop a head (blindness)
- Roots are swollen in to large spindle shaped tumor like galls
- Common in wet soils with a low pH (acidic)
- More information on Club Root
5 of 7
Cabbage/Green Peach/Turnip Aphid
Brevicoryne brassicae, Myzus persicae, Lipaphis erysimi
- Leaves become yellow and curled
- Plants are stunted and head may be deformed
- 1/16 to 1/8 inch long, soft-bodied and pear-shaped
- Aphids are present throughout the growing season
- More information on Aphids
6 of 7
Cabbage Maggot
Delia radicum
- Leaves turn yellow and may wilt
- Maggot feeds on roots
- Plants may be stunted
- Maggot is legless and yellow-white in color
- Present in early May and mid-June
- More information on Cabbage Maggot
7 of 7
Nitrogen Deficiency
- Leaves are pale yellow
- Leaf discoloration starts in lower older leaves
- More information on Nitrogen Deficiency