Extension > Garden > Diagnose a problem > What's wrong with my plant? > Vegetable > Cabbage > Discolored head
Cabbage > Head > Discolored head
1 of 5
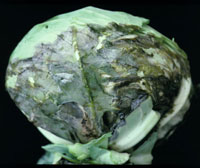
Downy Mildew
Peronospora parasitica
- Numerous black sunken spots can form on infected heads
- Gray-white sunken leaf spots which are often angular and restricted by the leaf veins
- Leaf tissue around the spots turns yellow
- Fuzzy gray growth can be seen on the underside of the leaves
- Disease is common in cool wet weather
- More information on Downy Mildew
2 of 5
Black Rot
Xanthomonas campestris
- Yellow V-shaped lesions develop on margin of leaves, the point of the v follows a vein towards the base of the leaf
- As infection continues, leaves wilt, turn yellow and eventually turn brown and die
- Black veins can be seen in infected leaves, petioles and stems
- Sticky yellowish liquid bacterial ooze may be seen if infected veins are cut
- Disease favored by hot, humid conditions
- More information on Black rot
3 of 5
Fusarium Wilt (Yellows)
Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. conglutinans
- Plant has a yellowish-green overall color that often occurs only on one side of the plant
- Lower leaves yellow first, yellowing progresses up the plant
- Affected leaves wilt, eventually turn brown, become dry and brittle, and may fall off
- Stem and midrib of the leaf curve to one side
- Veins in affected leaves are yellowish brown
4 of 5
Bottom Rot/Head Rot
Rhizoctonia solani
- Bottom of lower leaf develops sunken, black, and elliptical lesions parallel to the midrib of the leaf
- Dark cobweb-like or cotton-like fungal growth develops between diseased leaves
- Leaves turn yellow/brown and wilt
- Disease may be limited to the lowest leaves or may start at the bottom of the plant and move up through wrapper leaves into the cabbage head
5 of 5
Calcium Deficiency
- Browning may only be evident if head is cut open
- Younger leaves show signs of browning at the tips
- More information on Calcium Deficiency