Extension > Garden > Diagnose a problem > What's wrong with my plant? > Vegetable > Potato > Stunted plant
Potato > Whole plant > Stunted plant
1 of 4
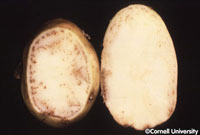
Potato Leaf Roll Virus (PLRV)
- Plants are stunted
- Leaves are cupped upward and yellow (white potato) or reddish (red potato)
- Leaves become leathery and dry as infection progresses
- Brown to black flecks can be seen in a net like pattern when the tuber is cut open
- More information on Potato Leaf Roll Virus (PLRV)
2 of 4
Fusarium Dry Rot
Fusarium sp.
- Plant may not emerge, or may emerge small and weak
- Tuber surface has sunken dark spots, eventually becoming wrinkled in concentric rings
- In storage, tuber develops a dry decayed cavity often with white fluffy fungal growth or pink to yellow spores inside
- More information on Fusarium Dry Rot
3 of 4
Blackleg and Soft Rot
Pectobacterium carotovora
- In severe cases, plant is stunted, with yellow and wilted leaves
- Seed potato may rot in the soil, plants do not emerge
- Brown to black slimy sunken lesions on stems, most common starting at the soil line
- Tuber flesh is white, soft and rotted. In severe cases the entire tuber rots away, leaving on the skin
- Favored by cool wet weather
- More information on Blackleg and Soft Rot
4 of 4
Black Scurf/Rhizoctonia Canker
Rhizoctonia solani
- Delayed or no emergence, have few stems, and poor growth
- Small hard black spots stick to the skin of the tuber like dirt that won't wash off
- Underground stems and roots have brown, sunken dry spots
- Tuber production is low, tubers may be small and deformed
- In severe cases, small green tubers form on the stem above ground
- Stem has a white to gray flaky growth just above the soil line.
- Most problematic in cool wet soils
- More information on Black Scurf/Rhizoctonia Canker