Extension > Garden > Diagnose a problem > What's wrong with my plant? > Vegetable > Tomato > Spots on fruit
Tomato > Fruit > Spots on fruit
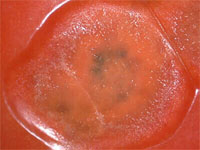
1 of 9
Early Blight
Alternaria solani
- Infects leaves, stems and fruit
- Black leathery spots on fruit start on stem end
- Dark irregular leaf spots, often surrounded by yellow tissue
- Sunken dark round stem lesion with concentric circles inside
- Occurs in warm wet weather, common at the end of summer
- More information on managing plant diseases in the home garden
2 of 9
Anthracnose
Colletotrichum coccodes
- Infections are visible only on ripe and over ripe tomatoes
- Fruit spots are sunken and round
- Mature fruit spots have a black center
- Fruit spots produce pink spores with moisture
- No visible spots on leaves and stems
- More information on managing plant diseases in the home garden
3 of 9
Blossom End Rot
Abiotic
- Affects only fruit
- The bottom of the tomato turns tan and soft, then black, sunken, and rotten
- Fruit may look short or stumpy, not fully expanded due to rot
- Common when water levels vary from irrigation or drought followed by rain
- More information on Blossom End Rot
4 of 9
Alternaria Fruit Rot
Alternaria alternata
- Sunken round to irregular spot on fruit
- Center of the spot is fuzzy and black
- Spots occur anywhere on fruit, often on the sides or shoulders
- Can occur on ripe or green fruit
- More information on managing plant diseases in the home garden
5 of 9
Late Blight
Phytophthora infestans
- Irregular water-soaked lesions on leaves, turn olive then brown
- Leaves, stems and petioles turn brown and shrivel
- Fruit spot is round olive colored, can cover whole fruit
- Infected tissue is covered with white mycelia is wet weather
- Disease spreads very rapidly in cool wet weather
- More information on managing plant diseases in the home garden
6 of 9
Bacterial Speck
Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato
- Leaves have small (2 mm) black spots surrounded by yellow or light green halo
- Green and red fruit have small black spots (1 to 2 mm)
*Best way to distinguish from bacterial spot - Occurs in cool wet weather 64° to 75° F
- Difficult to see bacterial streaming
- More information on managing plant diseases in the home garden
7 of 9
Bacterial Spot
Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria
- Leaves have small (1 mm) black spots surrounded by yellow or light green halo
- Green and red fruit have large corky black spots (4 to 5 mm)
*Best way to distinguish from bacterial speck - Fruit spots may have a white greasy looking halo
- Occurs in warm wet weather 75° to 86° F
- Difficult to see bacterial streaming
- More information on managing plant diseases in the home garden
8 of 9
Sunscald
Abiotic
- Affects fruit, young leaves and stems
- Occurs only on tissue exposed to the sun
- Fruit turns tan or white on exposed side, may dry out and appear wrinkled
- Young leaves of transplants turn grey with irregular bands on the lower side
- Young stems of transplants turn white on exposed side only
- More information on Sunscald
9 of 9
Virus
Cucumber mosaic virus, tomato mosaic virus, tomato
spotted wilt virus and more
- Leaves are mottled with yellow and light green patches
- Leaves are misshapen; unusually long and thin like a shoestring or curled and deformed
- Fruit have yellow blotches or brown rings
- Plants are stunted even when neighboring plants look healthy and tall
- More information on managing plant diseases in the home garden